Electricity plays a crucial role in our daily lives, and understanding UK house voltage is essential for homeowners. Whether you're dealing with electrical installations, troubleshooting issues, or simply curious about the electrical system in your home, knowing the basics of UK house voltage can be beneficial. In this article, we will delve into the details of UK house voltage, including its standard measurements, safety considerations, and practical applications.
Electricity powers our modern world, enabling us to use appliances, lighting, and electronics effortlessly. However, not everyone understands the intricacies of how electricity works within homes. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of UK house voltage, ensuring that you have the necessary knowledge to make informed decisions regarding your home's electrical system.
Whether you're a homeowner, a DIY enthusiast, or simply someone interested in learning more about electricity, this guide will serve as a valuable resource. We'll cover everything from the basics of UK house voltage to advanced topics such as voltage fluctuations, safety measures, and energy efficiency tips.
Read also:Smashing The Pool Noodler The Ultimate Guide To Mastering This Fun Water Activity
Table of Contents
- What is the Standard Voltage in UK Homes?
- A Brief History of Electricity in the UK
- Understanding Voltage Fluctuations in UK Homes
- Safety Measures for Handling UK House Voltage
- Impact of UK House Voltage on Household Appliances
- Improving Energy Efficiency with UK House Voltage
- Voltage Regulation Techniques
- Components of the Electrical System in UK Homes
- Troubleshooting Common Voltage Issues
- Conclusion and Final Thoughts
What is the Standard Voltage in UK Homes?
In the UK, the standard house voltage is set at 230 volts, with a tolerance of ±10%. This means that the voltage supplied to homes can range between 216 volts and 242 volts. The UK adheres to this standard as part of the European Union's regulations on electricity supply. This voltage level ensures compatibility with most household appliances and devices designed for use in the UK.
Key points:
- Standard voltage: 230 volts
- Tolerance range: ±10%
- Compatibility with EU standards
Why is the Standard Voltage Set at 230V?
The decision to standardize the voltage at 230V was made to align with European norms and improve efficiency in power distribution. This voltage level strikes a balance between safety and efficiency, ensuring that electrical devices operate optimally while minimizing energy losses during transmission.
A Brief History of Electricity in the UK
The history of electricity in the UK dates back to the late 19th century when the first public electricity supply was introduced in 1881. Over the years, the UK has made significant advancements in its electrical infrastructure, leading to the development of a robust and reliable power grid. Understanding this history provides valuable context for appreciating the current standards of UK house voltage.
Key Milestones in UK Electricity History
Important developments include:
- 1881: The first public electricity supply in Godalming, Surrey
- 1926: Establishment of the Central Electricity Board
- 1950s: Expansion of the National Grid
- 2000s: Focus on renewable energy sources
Understanding Voltage Fluctuations in UK Homes
Voltage fluctuations can occur in UK homes due to various factors, including weather conditions, high demand, or faulty electrical components. While minor fluctuations are generally harmless, significant deviations from the standard voltage can damage appliances and pose safety risks. It's important for homeowners to be aware of these fluctuations and take appropriate measures to mitigate them.
Read also:Best Remote Monitoring With Raspberry Pi Your Ultimate Guide
Common Causes of Voltage Fluctuations
Some of the most common causes include:
- Storms and lightning strikes
- High electricity demand during peak hours
- Faulty wiring or electrical equipment
Safety Measures for Handling UK House Voltage
Safety should always be a top priority when dealing with electricity. Proper handling of UK house voltage involves adhering to safety guidelines, using protective equipment, and ensuring that all electrical installations comply with regulations. Homeowners can also take additional steps to safeguard their homes against electrical hazards.
Essential Safety Tips
Follow these tips to ensure safety:
- Hire licensed electricians for installations and repairs
- Install residual current devices (RCDs) for protection
- Regularly inspect and maintain electrical systems
Impact of UK House Voltage on Household Appliances
The standard UK house voltage of 230V ensures that most household appliances function efficiently. However, appliances designed for different voltage standards may require adaptors or transformers to operate safely. Understanding the voltage requirements of your appliances can help prevent damage and ensure optimal performance.
Appliances Designed for UK Voltage
Common appliances include:
- Kitchen appliances: ovens, microwaves, refrigerators
- Electronics: TVs, computers, smartphones
- Heating systems: electric heaters, boilers
Improving Energy Efficiency with UK House Voltage
Energy efficiency is a growing concern for many homeowners, and understanding UK house voltage can help in making informed decisions about energy usage. By optimizing electrical systems and appliances, homeowners can reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills. Implementing energy-saving practices can also contribute to environmental sustainability.
Practical Energy-Saving Tips
Consider these tips:
- Upgrade to energy-efficient appliances
- Use smart power strips to eliminate standby power
- Install LED lighting to reduce energy consumption
Voltage Regulation Techniques
Effective voltage regulation is essential for maintaining a stable electrical supply in UK homes. Various techniques and devices are available to regulate voltage, ensuring that it remains within the acceptable range. Homeowners can invest in voltage regulators or consult with professionals to address specific voltage issues.
Types of Voltage Regulators
Popular options include:
- Automatic voltage regulators (AVRs)
- Stabilizers for sensitive electronics
- Smart grid technologies for advanced regulation
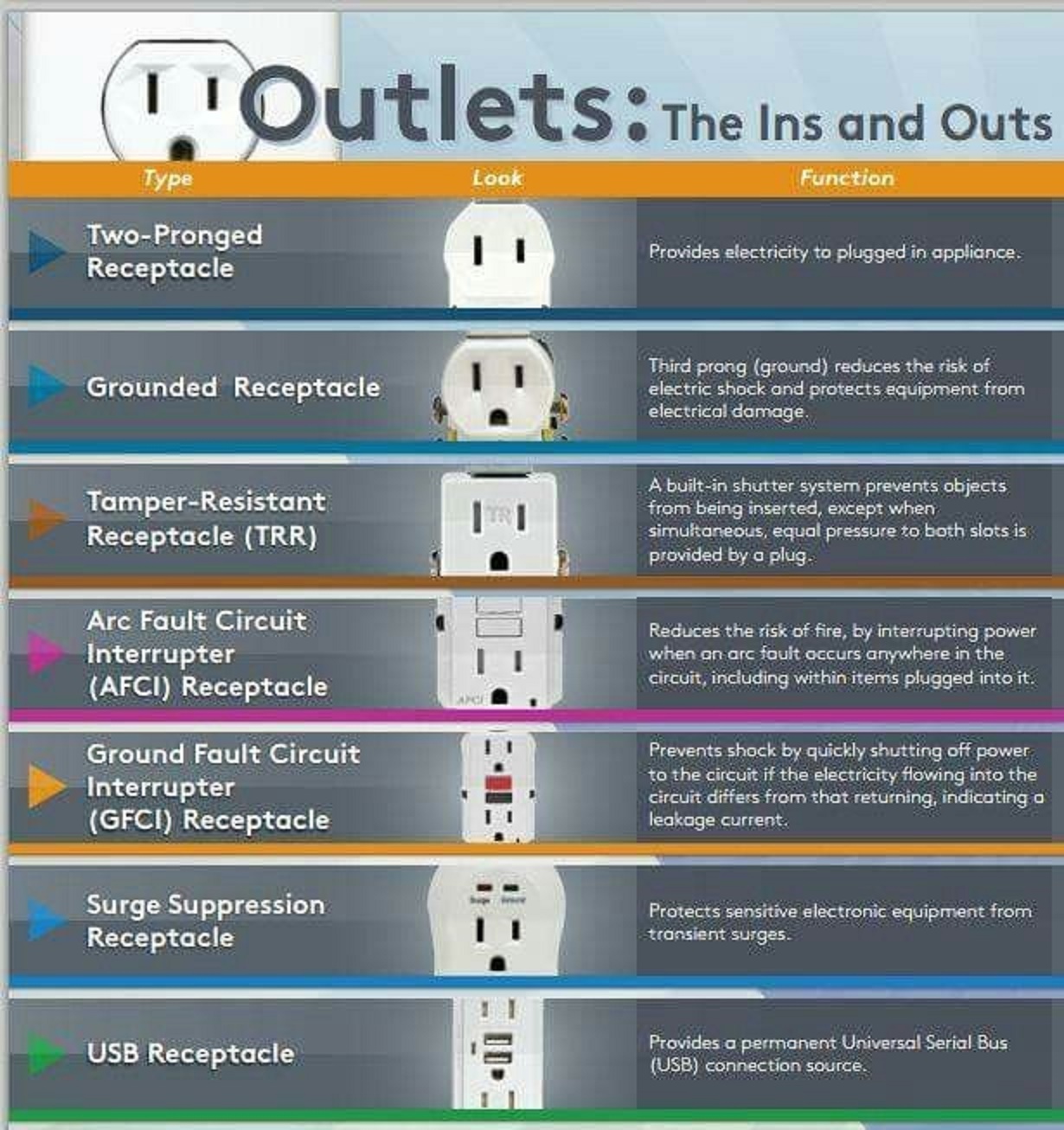
Components of the Electrical System in UK Homes
A typical UK home electrical system consists of several components that work together to distribute electricity safely and efficiently. Understanding these components can help homeowners identify potential issues and perform basic maintenance tasks. Key components include the main panel, circuit breakers, wiring, and outlets.
Main Components of the Electrical System
Key components include:
- Main panel: Distributes electricity to various circuits
- Circuit breakers: Protect against overloads and short circuits
- Wiring: Conducts electricity throughout the home
Troubleshooting Common Voltage Issues
Occasionally, homeowners may encounter voltage-related issues such as flickering lights, tripped circuit breakers, or appliances failing to operate correctly. Troubleshooting these problems involves identifying the root cause and taking appropriate corrective actions. Consulting a professional electrician is recommended for complex issues.
Steps for Troubleshooting
Follow these steps:
- Check the main panel for tripped breakers
- Inspect wiring for signs of damage or wear
- Test outlets and appliances for functionality
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Understanding UK house voltage is crucial for homeowners who want to ensure the safety and efficiency of their electrical systems. From the standard voltage of 230V to voltage fluctuations and energy-saving practices, this guide has covered a wide range of topics related to electricity in UK homes. By staying informed and proactive, homeowners can enjoy reliable and safe electrical power.
Take Action: We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from the information provided. If you have any questions or need further clarification, feel free to leave a comment below. Additionally, explore our other articles for more insights on home improvement and electrical topics.
Data sources: UK Government, IEEE, US Department of Energy.